By: Greg Robidoux | Updated: 2017-04-04 | Comments (7) | Related: More >Constraints
SQL FOREIGN KEY Constraint. A FOREIGN KEY is a key used to link two tables together. A FOREIGN KEY is a field (or collection of fields) in one table that refers to the PRIMARY KEY in another table. The table containing the foreign key is called the child table, and the table containing the candidate key is called the referenced or parent table.
Sql Server Default Foreign Key Generation Logical
Problem
I need to create a Foreign Key relationship between two SQL Server tables and I would like to know how this is done using the SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) GUI as well as using T-SQL scripts. I already have the tables created, but how do I create the Foreign Key relationship.
Solution
Creating a Foreign Key relationship should be a pretty straightforward task, but understanding how to use the GUI to do this is not as simple as you might think.
Let's say we have these two tables in our database.
We want to create a Foreign Key relationship between Product.ProductCategoryID and ProductCategory.ProductCategoryID to make sure the ProductCategoryID is a valid option for any entries entered into the Product table.
To help with understanding the relationships, ProductCategory will be the referenced table and Product will be the referencing table.
When creating a Foreign Key there are a few options to enforce rules when changes are made to the referenced table:
- Delete Rule - this determines what happens if the record is deleted in the referenced table.
- Update Rule - this determines what happens if the row key is updated in the referenced table.
The options for the Delete and Update rules are:
- NO ACTION - if the change breaks the referential integrity, the change is rolled back.
- CASCADE - the change should also occur on the referencing table. If it is for DELETE the referencing rows will be deleted too. If this if for an UPDATE the referencing table row values will be updated to match the new value.
- SET NULL - the value in the referencing table should be set to NULL as long as NULL values are allowed on that column in the referencing table. If not, the change is rolled back.
- SET DEFAULT - the value in the referencing table would be set to a default value. This value would also need to exist in the referenced table. If the value does not exist in the referenced table, the change would be rolled back.
Create Foreign Key Using T-SQL
To create the Foreign Key using T-SQL, the statement would be written as follows. This is showing that we want to CASCADE the changes for both DELETEs and UPDATEs.
Here is a description for each line above:
- Since the Product table already exists, we are using the ALTER TABLE command on the dbo.Product table.
- Foreign Keys are constraints, so we are adding a Constraint of type Foreign Key named FK_Product_ProductCategoryID using the ProductCategoryID column
- The Foreign Key references table dbo.ProductCategory using the ProductCategoryID column
- For the DELETE rule we are using CASCADE
- For the UPDATE rule we are using CASCADE
That's all there is to it.
Create Foreign Key Using SSMS GUI
To create a Foreign Key using the SSMS GUI, using Object Explorer select the referencing table dbo.Product, go to Keys, right click on Keys and select New Foreign Key...:
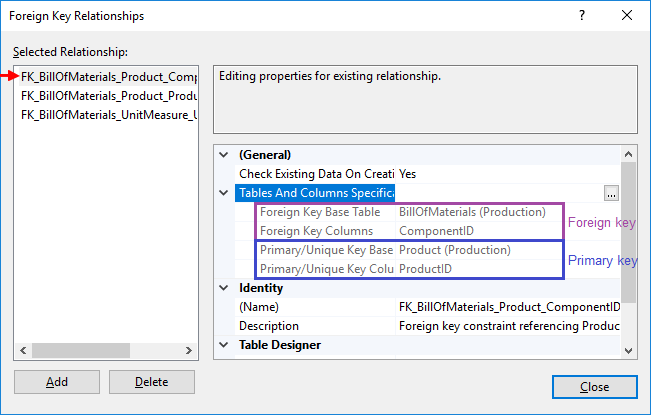
The table designer will open as well as a new window like below. Click on the ellipse (...) next to Tables and Columns Specification.
Another window will open like below.
We can change the Relationship Name (Foreign Key name) and also need to select the appropriate tables and columns. So on the left we select the referenced table ProductCategory and underneath we select the ProductCategoryID column. On the right, the referencing table Product is already selected, but underneath we need to select the column ProductCategoryID. After making the changes, click OK.
At this point we are back to the first Foreign Key screen that we saw. If you scroll down on the right pane, we can see the Delete and Update rules as shown in the image below. Select the appropriate values from the dropdown list.
You can see below there are two other options in the GUI as shown below:
- Enforce For Replication - if you are using replication and don't want the foreign keys enforced at the subscriber for the replicated data you would select No.
- Enforce Foreign Key Constraint - if you do not want to the foreign key to be checked you would select No. Setting this to No defeats the purpose of having a foreign key setup.
Now click Close to accept the Foreign Key changes.
To actually save the changes to the database, you can click on the Save button in SSMS, press Ctrl-S or use the SSMS menu and select File > Save Product (will be table name you are changing to save the Foreign Key constraint.
Reviewing the New Foreign Key
After the Foreign Key has been created, we can see it in Object Explorer as shown below. You can right click on the Foreign Key and either generate a script, modify it, delete it or rename it.
Next Steps
- Next time you are creating a Foreign Key, refer to this simple tip.
Last Updated: 2017-04-04
About the author
View all my tips
By: Rick Dobson | Updated: 2017-03-16 | Comments (4) | Related: More >Constraints
Problem
I have administrator responsibility for some legacy SQL Server databases that I did not create and do not use much personally. I have been charged with listing the SQL Server foreign keys within these databases. Can you present some different approaches to developing this kind of information as well as ways of validating the information generated by the different approaches?
Solution
It is relatively easy to find queries strewn across the Internet that claim to enumerate the foreign keys in a SQL Server database along with information about them. The best approach may depend on your personal preferences and needs as well as the type of databases for which you need to enumerate foreign keys.
For SQL Server databases, there are two common approaches to enumerating foreign keys.
- A traditional one is to use system tables that can enumerate tables with foreign keys as well as the tables that they reference.
- Queries based on INFORMATION_SCHEMA views are an alternative approach that may also be suitable for different types of databases than just SQL Server.
It is important to understand that foreign keys are defined in scripts; see this tip for sample T-SQL code and SSMS-based manual techniques for creating and specifying foreign keys. By examining the scripts for foreign keys in a database, you can verify how the foreign keys for a table are defined. While examining the scripts for individual tables can be tedious, it can also definitively verify a foreign key relationship. In addition, this kind of validation can give you helpful insights about how to define foreign keys in other databases.
A Quick Review of Foreign Keys
A foreign key is typically based on a set of one or more columns in a child table that references primary or unique key columns in a parent table. You can also define a foreign key relationship among two or more columns in the same table. In both scenarios, there is a referenced relationship so that the referencing column values match referenced column values. Also, referenced values cannot typically be removed from their columns without violating the foreign key relationship in a child set of column(s).
Foreign keys will always have names. The names are called foreign key constraints. You can designate the name for a foreign key constraint in a CREATE TABLE statement or ALTER TABLE statement with the CONSTRAINT keyword. You can use the CONSTRAINT keyword for naming a constraint at the same time that you create the constraint with the FOREIGN KEY and REFERENCES keywords. If you do not explicitly assign a foreign key name, then SQL SERVER will implicitly assign one. Well-constructed constraint names can provide useful information about foreign keys when they are enumerated.
SQL Server optionally allows action settings for designating how changes to referenced column values can impact referencing column values. A prior MSSQLTips.com article describes the syntax and operation of these action settings. For example, you can still maintain referential integrity when deleting a referenced column value with matching referencing column values if you specify an ON DELETE CASCADE option in the script for the foreign key. With this option, deleting a referenced column value in a parent set of columns also deletes all rows with matching values from a child (or referencing) set of columns. With the NO ACTION setting, neither updates nor deletes to values in the referenced columns are allowed if there are corresponding values in a referencing set of columns. The NO ACTION setting is enforced unless another action setting is explicitly designated.
For the purposes of this tip, constraint names are critical because they allow you to designate the foreign key relationships that the tip's code enumerates; each foreign key must have its own distinct name. It is also imperative to understand that foreign keys denote a relationship between a child set of columns and a parent set of columns. Finally, you may find it useful to have a general understanding of foreign key cascading action settings to know what they designate when foreign keys are enumerated.
Enumerating all foreign key constraints for the AdventureWorksDW2014 database
The following scripts illustrate how to enumerate all foreign key constraints for the AdventureWorksDW2014 sample database. The approaches coded in this section give you an overview of all the foreign key constraints within a database.
The first two lines reference the sample database. The first code block illustrates a system tables approach to enumerating foreign keys for the database. The second code block illustrates an INFORMATION_SCHEMA approach to enumerating foreign keys for the database. The trailing ORDER BY statement in both first and second code blocks facilitates comparisons between the result set rows from both queries.
The screen shot below shows the first 13 rows from the result set for each code block. Notice the two result set excerpts appear identical in content. Also, there is a total of 90 rows across both result sets - 45 each from the first and second blocks.
The FK_DimAccount_DimAccount constraint appears as the first row in both result sets. This constraint restricts values in the ParentAccountKey column to those in a previously input AccountKey column. The AccountKey column is the primary key for the DimAccount table, and therefore every row in the table has a unique AccountKey value. The ParentAccountKey value for a new row in the DimAccount table depends on the existence of a previously specified AccountKey value for another row in the same table. Any AccountKey value can have multiple rows depend on it through the ParentAccountKey value for the other rows. If an AccountKey value has one or more other rows with a ParentAccountKey value referencing it, then the referenced AccountKey value cannot be removed or changed in the table without corresponding changes in the ParentAccountKey values that reference it.
The first of the following two ALTER TABLE statements shows the code to define the FK_DimAccount_DimAccount constraint in the DimAccount table. Within the first ALTER TABLE statement, notice that the DimAccount table name appears in the ALTER TABLE clause as well as its REFERENCES clause. The second ALTER TABLE statement specifies a distinct check of the FK_DimAccount_DimAccount constraint outside of the preceding ALTER TABLE statement. This second distinct check can be especially relevant in cases where foreign key constraints are temporarily disabled and later re-enabled. For more detail on foreign key checking for disabled and re-enabled foreign keys (as well as related issues) see this summary.
Add Foreign Key Sql Server
The FK_DimCustomer_DimGeorgraphy constraint in the second row of the result sets below denotes a more typical type of foreign key. In this case, the referencing column of one table references a column in another table. The GeographyKey column from the DimCustomer table references the GeographyKey column from the DimGeography table. The GeorgraphyKey column serves as a primary key column in the DimGeography table and a foreign key column in the DimCustomer table. The FK_DimCustomer_DimGeorgraphy constraint forces referential integrity so that it is impossible to enter a new customer row in the DimCustomer table with a GeorgraphyKey value that does not already exist in the DimGeography table.
Here's a pair of scripts for adding the FK_DimCustomer_DimGeography constraint to the DimCustomer table and enforcing the constraint for each inserted or changed row. Notice that the first ALTER TABLE statement in this script references two different tables - DimCustomer in the ALTER TABLE clause and DimGeography in the REFERENCES clause. The value after the CONSTRAINT keyword designates the name of the foreign key constraint. The FOREIGN KEY keyword specifies the referencing column in the DimCustomer referencing table. The table name after the REFERENCES keyword denotes the referenced table -- DimGeography. The column name in parentheses after the table name denotes the referenced column -- GeographyKey.
The constraints on the first and second rows of a result sets below can exist for either OLTP or OLAP databases. However, OLAP databases, such as the AdventureWorksDW2014 database, typically rely heavily on foreign keys. The FACT tables in an OLAP database usually reference one or more DIM tables shared across multiple FACT tables. This forces the FACT tables to be referentially consistent for the DIM tables that they reference.
The thirteenth row in the following two result sets denotes a constraint for a FACT table, FactCurrencyRate that references a DIM table, DimCurrency. The CurrencyKey column in each row of the FactCurrencyRate table must exist in the CurrencyKey column of the DimCurrency table. The constraint denoting this foreign key relationship has the name FK_FactCurrencyRate_DimCurrency.
Enumerating foreign key constraints for a designated referenced table
The following scripts illustrate how to enumerate a select set of foreign key constraints that are dependent on a particular referenced table. The first approach demonstrates the sys table syntax and the second approach reveals INFORMATION_SCHEMA syntax. This example uses the AdventureWorks2014 database, which is an OLTP database in contrast to the OLAP database in the preceding example. Both OLTP and OLAP databases take advantage of the same approach for enumerating all foreign key constraints. To select a subset of all foreign key constraints for a particular referenced table, all you need to do is add a WHERE clause designating the referenced table name.
With just the default NO ACTION setting, there is mutual constraining between referenced and referencing tables in a foreign key relationship. Referencing tables cannot accept a new referencing column value that is not already a primary key value or a unique key value in the referenced table. Similarly, referenced tables cannot change a referenced column value that is in a referencing table; to do so would violate the integrity of the foreign key. So long as the changes that you want to make to a referenced table are not among those in the referencing columns, then you can change them in the referenced table without any concern for impact on the foreign key integrity.
By using cascading delete and update settings, you can make changes to a referenced table even when a referencing table shares referencing column values with a referenced table. Cascading delete or update referential action settings can propagate actions made to a referenced table to referencing tables to maintain the integrity of foreign key references.
The following screen shot displays the output from each of the two approaches for listing referencing tables for the SalesOrderHeader table in the AdventureWorks2014 database. The two tables that reference the SalesOrderHeader table are the SalesOrderDetail table and the SalesOrderHeaderSalesReason table. Cascading delete actions are specified for both referencing tables. The cascading delete action setting means that any SalesOrderID value deleted from the SalesOrderHeader table will result in deleted rows from both SalesOrderDetail and SalesOrderHeaderSalesReason tables for rows with a matching SalesOrderID value. In contrast, no cascading action is specified for updates. Therefore, any attempt to update a SalesOrderID value in the SalesOrderHeader table will be prohibited for foreign key check reasons if that SalesOrderID value also exists in either the SalesOrderDetail or SalesOrderHeaderSalesReason tables.
The following ALTER TABLE statements illustrate the syntax for denoting the foreign key relationship of the SalesOrderDetail table to the SalesOrderHeader table. Notice that the first ALTER TABLE statement includes an ON DELETE CASCADE clause. With this clause, if a SalesOrderID value is deleted from the SalesOrderHeader table, then all rows in the SalesOrderDetail table with a matching SalesOrderID value will also be deleted.
No cascading update action is specified along with the preceding ON DELETE CASCADE setting. SQL Server does permit an ON UPDATE CASCADE clause, but you will notice that it was not used in this example. Many developers argue you should not update primary key values. In this example, that rule makes sense since SalesOrderID values in the SalesOrderHeader table are identity values. When the primary key for the referenced table is a 'natural' value that is not an arbitrary number but has some meaning for the row, such as product name type, then the use of the ON UPDATE CASCADE clause may be appropriate as the number of product types expand. For example, the same product can belong to different product types before and after a product line expansion and reorganization.
Next Steps
- Try the code samples in this tip for listing all foreign keys or a subset of foreign keys with your own databases. Focus on thinking about foreign keys as referencing columns from referencing tables that point at referenced columns from referenced tables.
- Keep in mind that referenced and referencing column names can have different names. This is necessarily the case when the referencing column and referenced column are from the same table. When the referencing table is different from the referenced table, the referencing column and referenced column can have the same or different names. The code examples in this tip do not require referencing column names to match referenced column names.
- When time permits, I encourage you to script tables participating in foreign key relationships. This can help you understand how they are used in an application. Additionally, it may give you insights about best practices and common practices within an organization for using foreign keys.
- This tip closes with a reminder that foreign keys are an advanced database development topic. This tip narrowly focuses on techniques for enumerating foreign keys within a database. Other foreign key topics are covered only to help you understand the columns of results sets for enumerated foreign keys within a database. Furthermore, there are many foreign key issues that are not covered at all within this tip. Hopefully, this tip will motivate others to author additional tips on foreign keys issues not covered here.
Last Updated: 2017-03-16
Sql Server Default Foreign Key Generation Logic 2017
About the author
View all my tips